FDA records indicate that there are no current recalls for this drug.
Are you a medical professional?
Trending Topics
Ammonian 13 N 13 Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
There is currently no warning information available for this product. We apologize for any inconvenience.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
Ammonia N 13 Injection is indicated for diagnostic Positron Emission Tomography (PET) imaging of the myocardium under rest or pharmacologic stress conditions to evaluate myocardial perfusion in patients with suspected or existing coronary artery disease.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
Ammonia N 13 Injection is a positron emitting radiopharmaceutical that is used for diagnostic purposes in conjunction with positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. The active ingredient, [13N] ammonia, has the molecular formula of 13NH3with a molecular weight of 16.02, and has the following chemical structure:
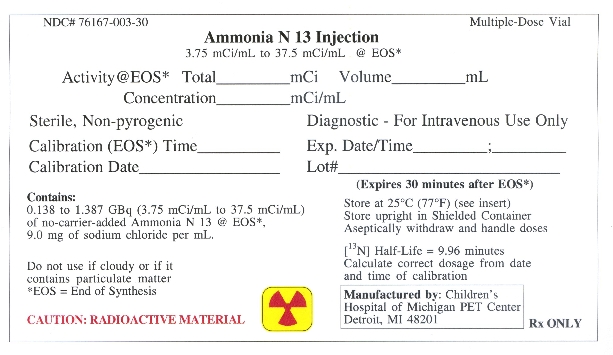
Ammonia N 13 Injection is provided as a ready to use sterile, pyrogen-free, clear and colorless solution. Each mL of the solution contains between 0.138 GBq to 1.387 GBq (3.75 mCi to 37.5mCi) of [13N] ammonia, at the end of synthesis (EOS) reference time, in 0.9% aqueous sodium chloride. The pH of the solution is between 4.5 to 7.5. The recommended dose of radioactivity (10-20 mCi) is associated with a theoretical mass dose of 0.05-0.1 picomoles (8.47-16.94 picograms) of ammonia.
Nitrogen N13 decays by emitting positron to Carbon C13 (stable) and has a physical half-life of 9.96 minutes. The principal photons useful for imaging are the dual 511 keV gamma photons that are produced and emitted simultaneously in opposite direction when the positron interacts with an electron (Table 2).
| Radiation/Emission | %Per Disintegration | Energy |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Positron(β+) | 100 | 1190 keV (Max.) |
| Gamma(±)* | 200 | 511 keV |
The specific gamma ray constant (point source air kerma coefficient) for nitrogen N13 is 5.9 R/hr/mCi (1.39 x 10-6 Gy/hr/kBq) at 1 cm. The half-value layer (HVL) of lead (Pb) for 511 keV photons is 4 mm. Selected coefficients of attenuation are listed in Table 3 as a function of lead shield thickness. For example, the use of 39 mm thickness of lead will attenuate the external radiation by a factor of about 1000.
| Shield Thickness (Pb) mm | Coefficient of Attenuation |
|---|---|
| 4 | 0.5 |
| 8 | 0.25 |
| 13 | 0.1 |
| 26 | 0.01 |
| 39 | 0.001 |
| 52 | 0.0001 |
Table 4 lists fractions remaining at selected time intervals from the calibration time. This information may be used to correct for physical decay of the radionuclide.
| Minutes | Fraction Remaining |
|---|---|
|
|
| 0* | 1.000 |
| 5 | 0.706 |
| 10 | 0.499 |
| 15 | 0.352 |
| 20 | 0.249 |
| 25 | 0.176 |
| 30 | 0.124 |
Sources
Ammonian 13 N 13 Manufacturers
-
Children’s Hospital Of Michigan
![Ammonian 13 N 13 (Ammonia N-13) Injection [Children’s Hospital Of Michigan]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Ammonian 13 N 13 | Children's Hospital Of Michigan
![Ammonian 13 N 13 (Ammonia N-13) Injection [Children’s Hospital Of Michigan] Ammonian 13 N 13 (Ammonia N-13) Injection [Children’s Hospital Of Michigan]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
2.1 Rest Imaging Study Aseptically withdraw Ammonia N 13 Injection from its container and administer 10-20 mCi (0.368 – 0.736 GBq) as a bolus through a catheter inserted into a large peripheral vein. Start imaging 3 minutes after the injection and acquire images for a total of 10-20 minutes. 2.2 Stress Imaging Study If a rest imaging study is performed, begin the stress imaging study 40 minutes or more after the first Ammonia N 13 injection to allow sufficient isotope decay. Administer a pharmacologic stress-inducing drug in accordance with its labeling. Aseptically withdraw Ammonia N 13 Injection from its container and administer 10-20 mCi (0.368 – 0.736 GBq) of Ammonia N 13 Injection as a bolus at 8 minutes after the administration of the pharmacologic stress-inducing drug. Start imaging 3 minutes after the Ammonia N 13 Injection and acquire images for a total of 10-20 minutes. 2.3 Patient PreparationTo increase renal clearance of radioactivity and to minimize radiation dose to the bladder, ensure that the patient is well hydrated before the procedure and encourage voiding as soon as a study is completed and as often as possible thereafter for at least one hour.
2.4 Radiation DosimetryThe converted radiation absorbed doses in rem/mCi are shown in Table 1. These estimates are calculated from the Task Group of Committee 2 of the International Commission on Radiation Protection.1
Table 1: N 13 Absorbed Radiation Dose Per Unit Activity (rem/mCi) for Adults and Pediatric Groups. Organ Age (years) Adult 15 10 5 1 * Upper large intestine, † Lower large intestine Adrenals 0.0085 0.0096 0.016 0.025 0.048 Bladder wall 0.030 0.037 0.056 0.089 0.17 Bone surfaces 0.0059 0.0070 0.011 0.019 0.037 Brain 0.016 0.016 0.017 0.019 0.027 Breast 0.0067 0.0067 0.010 0.017 0.033 Stomach wall 0.0063 0.0078 0.012 0.019 0.037 Small intestine 0.0067 0.0081 0.013 0.021 0.041 *ULI 0.0067 0.0078 0.013 0.021 0.037 †LLI 0.0070 0.0078 0.013 0.020 0.037 Heart 0.0078 0.0096 0.015 0.023 0.041 Kidneys 0.017 0.021 0.031 0.048 0.089 Liver 0.015 0.018 0.029 0.044 0.085 Lungs 0.0093 0.011 0.018 0.029 0.056 Ovaries 0.0063 0.0085 0.014 0.021 0.041 Pancreas 0.0070 0.0085 0.014 0.021 0.041 Red marrow 0.0063 0.0078 0.012 0.020 0.037 Spleen 0.0093 0.011 0.019 0.030 0.056 Testes 0.0067 0.0070 0.011 0.018 0.035 Thyroid 0.0063 0.0081 0.013 0.021 0.041 Uterus 0.0070 0.0089 0.014 0.023 0.041 Other tissues 0.0059 0.0070 0.011 0.018 0.035 2.5 Drug Handling Inspect Ammonia N 13 Injection visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not administer Ammonia N 13 Injection containing particulate matter or discoloration; dispose of these unacceptable or unused preparations in a safe manner, in compliance with applicable regulations. Wear waterproof gloves and effective shielding when handling Ammonia N 13 Injection. Use aseptic technique to maintain sterility during all operations involved in the manipulation and administration of Ammonia N 13 Injection. The contents of each vial are sterile and non-pyrogenic. Use appropriate safety measures, including shielding, consistent with proper patient management to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure to the patient, occupational workers, clinical personnel, and other persons. Radiopharmaceuticals should be used by or under the control of physicians who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radionuclides, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate governmental agency authorized to license the use of radionuclides. Before administration of Ammonia N 13 Injection, assay the dose in a properly calibrated dose calibrator.
Login To Your Free Account