Meprobamate Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
Drug Dependence
Physical dependence, psychological dependence, and abuse haveoccurred. When chronic intoxication from prolonged use occurs, itusually involves ingestion of greater than recommended doses and ismanifested by ataxia, slurred speech, and vertigo. Therefore, carefulsupervision of dose and amounts prescribed is advised, as well asavoidance of prolonged administration, especially for alcoholics andother patients with a known propensity for taking excessive quantitiesof drugs.
Sudden withdrawal of the drug after prolonged and excessive use mayprecipitate recurrence of pre-existing symptoms such as anxiety,anorexia, insomnia, or withdrawal reactions such as vomiting, ataxia,tremors, muscle twitching, confusional states, hallucinosis, andrarely, convulsive seizures. Such seizures are more likely to occur inpersons with central nervous system damage or pre-existent or latentconvulsive disorders. Onset of withdrawal symptoms occurs usuallywithin 12 to 48 hours after discontinuation of meprobamate;symptoms usually cease within the next 12 to 48 hours.
When excessive dosage has continued for weeks or months, dosageshould be reduced gradually over a period of one or two weeks ratherthan abruptly stopped. Alternatively, a long-acting barbiturate may besubstituted, then gradually withdrawn.
Potentially Hazardous Tasks
Patients should be warned that meprobamate may impair the mentaland/or physical abilities required for performance of potentiallyhazardous tasks such as driving or operating machinery.
Additive Effects
Since the effects of meprobamate and alcohol or meprobamate andother CNS depressants or psychotropic drugs may be additive,appropriate caution should be exercised with patients who take morethan one of these agents simultaneously.
Usage in Pregnancy and Lactation
An increased risk of congenital malformations associated with theuse of minor tranquilizers (meprobamate, chlordiazepoxide anddiazepam) during the first trimester of pregnancy has beensuggested in several studies. Because use of these drugs is rarelya matter of urgency, their use during this period should almostalways be avoided. The possibility that a woman of childbearingpotential may be pregnant at the time of institution of therapyshould be considered. Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant during therapy or intend to become pregnant theyshould communicate with their physician about the desirability ofdiscontinuing the drug.
Meprobamate passes the placental barrier. It is present both inumbilical cord blood at or near maternal plasma levels and inbreast milk of lactating mothers at concentrations two to four timesthat of maternal plasma. When use of meprobamate iscontemplated in breastfeeding patients, the drug's higherconcentration in breast milk as compared to maternal plasmashould be considered.
Usage in Children
Meprobamate tablets should not be administered to children underage six, since there is a lack of documented evidence for safety andeffectiveness in this age group.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
Meprobamate tablets are indicated for the management of anxietydisorders or for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety.Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usuallydo not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
The effectiveness of meprobamate tablets in long-term use, that is,more than 4 months, has not been assessed by systematic clinicalstudies. The physician should periodically reassess the usefulness ofthe drug for the individual patient.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
Meprobamate is awhite powder with a characteristic odor and a bittertaste. It is slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in acetone andalcohol, and sparingly soluble in ether. The structural formula of meprobamate is:
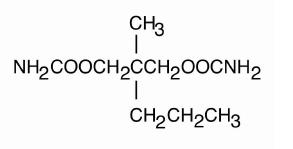
C9H18N2O4 M.W.218.25
Meprobamate Tablets USP 200 mg and 400 mg for oral administrationcontain the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose,sodium starch glycolate, pre-gelatinized starch, colloidal silicondioxide, stearic acid and magnesium stearate.
Sources




![Meprobamate Tablet [Taro Pharmaceuticals U.s.a., Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=4a9ad4f6-6826-4cb8-a097-2d2ea2c91d8b&name=meprobamate-02.jpg)
![Meprobamate Tablet [Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=e9aa3d4c-f2e9-4ca9-b563-85fac4024539&name=meprobamate-02.jpg)
![Meprobamate Tablet [Watson Laboratories, Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=a27d7877-38e4-4437-afd3-3d570c0dead1&name=meprobamate-tablets-2.jpg)
![Meprobamate Tablet [Alembic Pharmaceuticals Limited]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=a0891a32-105b-48bc-a246-5e179d2e7fa1&name=meprobamate-200mg.jpg)
![Meprobamate Tablet [Heritage Pharmaceuticals Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=223068d2-e7cc-4f15-8be3-30263ea5cbab&name=200mg-100.jpg)