FDA records indicate that there are no current recalls for this drug.
Are you a medical professional?
Trending Topics
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate And Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
Administration of sodium phosphate products prior to colonoscopy for colon cleansing has resulted in fatalities due to significant fluid shifts, severe electrolyte abnormalities, and cardiac arrhythmias. These fatalities have been observed in patients with renal insufficiency, in patients with bowel perforation, and in patients who misused or overdosed sodium phosphate products. It is recommended that patients receiving monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets be advised to adequately hydrate before, during, and after the use of monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets.
Considerable caution should be advised before monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets are used in patients with the following illnesses: severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/minute), congestive heart failure, ascites, unstable angina, gastric retention, ileus, acute bowel obstruction, pseudo-obstruction of the bowel, severe chronic constipation, bowel perforation, acute colitis, toxic megacolon, gastric bypass or stapling surgery, or hypomotility syndrome.
Consider performing baseline and post-colonoscopy labs (phosphate, calcium, potassium, sodium, creatinine, and BUN) in patients who may be at increased risk for serious adverse events, including those with history of renal insufficiency, history of-or at greater risk of-acute phosphate nephropathy, known or suspected electrolyte disorders, seizures, arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy, prolonged QT, recent history of a MI and those with known or suspected hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, and hypernatremia. Also if patients develop vomiting and/or signs of dehydration then measure post-colonoscopy labs (phosphate, calcium, potassium, sodium, creatinine, and BUN).
Renal Disease, Acute Phosphate Nephropathy, and Electrolyte Disorders
There have been rare, but serious, reports of renal failure, acute phosphate nephropathy, and nephrocalcinosis in patients who received oral sodium phosphate products (including oral sodium phosphate solutions and tablets) for colon cleansing prior to colonoscopy. These cases often resulted in permanent impairment of renal function and several patients required long-term dialysis. The time to onset is typically within days; however, in some cases, the diagnosis of these events has been delayed up to several months after the ingestion of these products. Patients at increased risk of acute phosphate nephropathy may include patients with the following: hypovolemia, baseline kidney disease, increased age, and patients using medicines that affect renal perfusion or function [such as diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and possibly nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Use monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets with caution in patients with impaired renal function, patients with a history of acute phosphate nephropathy, known or suspected electrolyte disturbances (such as dehydration), or people taking concomitant medications that may affect electrolyte levels (such as diuretics). Patients with electrolyte abnormalities such as hypernatremia, hyperphosphatemia, hypokalemia, or hypocalcemia should have their electrolytes corrected before treatment with monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets.
Seizures
There have been rare reports of generalized tonic-clonic seizures and/or loss of consciousness associated with use of sodium phosphate products in patients with no prior history of seizures. The seizure cases were associated with electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia) and low serum osmolality. The neurologic abnormalities resolved with correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities. Monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets should be used with caution in patients with a history of seizures and in patients at higher risk of seizure [patients using concomitant medications that lower the seizure threshold (such as tricyclic antidepressants), patients withdrawing from alcohol or benzodiazepines, or patients with known or suspected hyponatremia].
Cardiac Arrhythmias
There have been rare, but serious, reports of arrhythmias associated with the use of sodium phosphate products. Monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets should be used with caution in patients with higher risk of arrhythmias (patients with a history of cardiomyopathy, patients with prolonged QT, patients with a history of uncontrolled arrhythmias, and patients with a recent history of a myocardial infarction). Pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs should be considered in patients with high risk of serious, cardiac arrhythmias.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are indicated for cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy in adults 18 years of age or older.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablet is a purgative used to clean the colon prior to colonoscopy. Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are manufactured with a highly soluble tablet binder and does not contain microcrystalline cellulose (MCC). Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are white to off-white modified oval shaped, biconvex, bisect on one side and plain on the other debossed “N” on the left side of bisect and “03” on the right side of the bisect. Each Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablet contains 1.102 grams of monobasic sodium phosphate, USP and 0.398 grams of dibasic sodium phosphate, USP for a total of 1.5 grams of sodium phosphate per tablet. Inert ingredients include polyethylene glycol 8000; and magnesium stearate. Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablet is gluten-free.
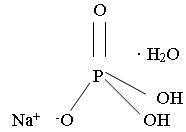
The structural and molecular formulae and molecular weights of the active ingredients are shown below:
Monobasic sodium phosphate, USP

Molecular Formula: NaH2PO4• H2O
Molecular Weight: 137.99
Dibasic sodium phosphate, USP

Molecular Formula: Na2HPO4
Molecular Weight: 141.96
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate and Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablets are for oral administration only.
Sources
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate And Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Manufacturers
-
Novel Laboratories, Inc.
![Monobasic Sodium Phosphate And Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablet [Novel Laboratories, Inc.]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Monobasic Sodium Phosphate And Dibasic Sodium Phosphate | Novel Laboratories, Inc.
![Monobasic Sodium Phosphate And Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablet [Novel Laboratories, Inc.] Monobasic Sodium Phosphate And Dibasic Sodium Phosphate Tablet [Novel Laboratories, Inc.]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
The recommended dose of monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets for colon cleansing for adult patients is 32 tablets (48 grams of sodium phosphate) taken orally with a total of 2 quarts of clear liquids in the following manner:
The evening before the colonoscopy procedure:
Take 4 monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids every 15 minutes for a total of 20 tablets.
On the day of the colonoscopy procedure:
Starting 3-5 hours before the procedure, take 4 monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets with 8 ounces of clear liquids every 15 minutes for a total of 12 tablets.
Patients should be advised of the importance of taking the recommended fluid regimen. It is recommended that patients receiving monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets be advised to adequately hydrate before, during, and after the use of monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets.
Patients should not use monobasic sodium phosphate and dibasic sodium phosphate tablets for colon cleansing within seven days of previous administration. No additional enema or laxative is required, and patients should be advised NOT to take additional agents, particularly those containing sodium phosphate.
Login To Your Free Account