Perphenazine Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Perphenazine is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis (see BOXED WARNING).
Tardive dyskinesia, a syndrome consisting of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements, may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Older patients are at increased risk for development of tardive dyskinesia. Although the prevalence of the syndrome appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women, it is impossible to rely upon prevalence estimates to predict, at the inception of antipsychotic treatment, which patients are likely to develop the syndrome. Whether antipsychotic drug products differ in their potential to cause tardive dyskinesia is unknown.
Both the risk of developing the syndrome and the likelihood that it will become irreversible are believed to increase as the duration of treatment and the total cumulative dose of antipsychotic drugs administered to the patient increase. However, the syndrome can develop, although much less commonly, after relatively brief treatment periods at low doses.
There is no known treatment for established cases of tardive dyskinesia, although the syndrome may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is withdrawn. Antipsychotic treatment itself, however, may suppress (or partially suppress) the signs and symptoms of the syndrome, and thereby may possibly mask the underlying disease process. The effect that symptomatic suppression has upon the long-term course of the syndrome is unknown.
Given these considerations, especially in the elderly, antipsychotics should be prescribed in a manner that is most likely to minimize the occurrence of tardive dyskinesia. Chronic antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients who suffer from a chronic illness that 1) is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs, and 2) for whom alternative, equally effective, but potentially less harmful treatments are not available or appropriate. In patients who do require chronic treatment, the smallest dose and the shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical response should be sought. The need for continued treatment should be reassessed periodically.
If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia appear in a patient on antipsychotics, drug discontinuation should be considered. However, some patients may require treatment despite the presence of the syndrome. (For further information about the description of tardive dyskinesia and its clinical detection, please refer to Information for Patients and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
A potentially fatal symptom complex, sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), has been reported in association with antipsychotic drugs. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmias).
The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. In arriving at a diagnosis, it is important to identify cases where the clinical presentation includes both serious medical illness (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever and primary central nervous system (CNS) pathology.
The management of NMS should include 1) immediate discontinuation of antipsychotic drugs and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy, 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring, and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for uncomplicated NMS.
If a patient requires antipsychotic drug treatment after recovery from NMS, the reintroduction of drug therapy should be carefully considered. The patient should be carefully monitored, since recurrences of NMS have been reported.
If hypotension develops, epinephrine should not be administered since its action is blocked and partially reversed by perphenazine. If a vasopressor is needed, norepinephrine may be used. Severe, acute hypotension has occurred with the use of phenothiazines and is particularly likely to occur in patients with mitral insufficiency or pheochromocytoma. Rebound hypertension may occur in pheochromocytoma patients.
Perphenazine products can lower the convulsive threshold in susceptible individuals; they should be used with caution in alcohol withdrawal and in patients with convulsive disorders. If the patient is being treated with an anticonvulsant agent, increased dosage of that agent may be required when perphenazine products are used concomitantly.
Perphenazine products should be used with caution in patients with psychic depression.
Perphenazine may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery; therefore, the patient should be warned accordingly.
Perphenazine products are not recommended for pediatric patients under 12 years of age.
Usage in Pregnancy
Safe use of perphenazine during pregnancy and lactation has not been established; therefore, in administering the drug to pregnant patients, nursing mothers, or women who may become pregnant, the possible benefits must be weighed against the possible hazards to mother and child.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)
A potentially fatal symptom complex, sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), has been reported in association with antipsychotic drugs. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmias).
The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. In arriving at a diagnosis, it is important to identify cases where the clinical presentation includes both serious medical illness (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever and primary central nervous system (CNS) pathology.
The management of NMS should include 1) immediate discontinuation of antipsychotic drugs and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy, 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring, and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for uncomplicated NMS.
If a patient requires antipsychotic drug treatment after recovery from NMS, the reintroduction of drug therapy should be carefully considered. The patient should be carefully monitored, since recurrences of NMS have been reported.
If hypotension develops, epinephrine should not be administered since its action is blocked and partially reversed by perphenazine. If a vasopressor is needed, norepinephrine may be used. Severe, acute hypotension has occurred with the use of phenothiazines and is particularly likely to occur in patients with mitral insufficiency or pheochromocytoma. Rebound hypertension may occur in pheochromocytoma patients.
Perphenazine products can lower the convulsive threshold in susceptible individuals; they should be used with caution in alcohol withdrawal and in patients with convulsive disorders. If the patient is being treated with an anticonvulsant agent, increased dosage of that agent may be required when perphenazine products are used concomitantly.
Perphenazine products should be used with caution in patients with psychic depression.
Perphenazine may impair the mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery; therefore, the patient should be warned accordingly.
Perphenazine products are not recommended for pediatric patients under 12 years of age.
Usage in Pregnancy
Safe use of perphenazine during pregnancy and lactation has not been established; therefore, in administering the drug to pregnant patients, nursing mothers, or women who may become pregnant, the possible benefits must be weighed against the possible hazards to mother and child.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
Perphenazine is indicated for use in the treatment of schizophrenia and for the control of severe nausea and vomiting in adults.
Perphenazine has not been shown effective for the management of behavioral complications in patients with mental retardation.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
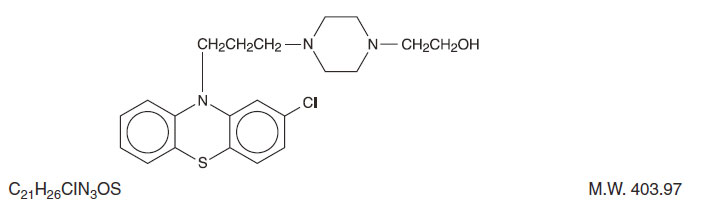
Perphenazine (4-[3-(2-chlorophenothiazin-10-yl)propyl]-1-piperazineethanol), a piperazinyl phenothiazine, having the chemical formula, C21H26CIN3OS. It is available as oral tablets containing 2 mg, 4 mg, 8 mg, and 16 mg of perphenazine.
Inactive ingredients: black iron oxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, sodium starch glycolate, talc, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide. Its structural formula is:
Sources




![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Contract Pharmacy Services-pa]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=f2c7e54b-ed7c-4d8f-a86d-5099a8b52f28&name=f2c7e54b-ed7c-4d8f-a86d-5099a8b52f28-02.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Sugar Coated [State Of Florida Doh Central Pharmacy]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=ad8193fb-4e3c-42e9-a4a8-49133650b86b&name=Perphenazine2mg(Qualitest).jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [State Of Florida Doh Central Pharmacy]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=ca1b6a78-739b-4e2a-9332-145c887fb2ff&name=Perphenazine16mg(Geneva).jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Sugar Coated [Qualitest Pharmaceuticals]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=d09dd18f-8db4-4fee-b51c-6aba56850103&name=perphenazine-2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Rebel Distributors Corp]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=2d821387-4b4f-4fe3-825e-750f49755baf&name=2d821387-4b4f-4fe3-825e-750f49755baf-02.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Ncs Healthcare Of Ky, Inc Dba Vangard Labs]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=6beb0c1a-9801-40d9-97d5-3488e603cc1a&name=perphenazine-2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet [Remedyrepack Inc. ]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=283636b7-0c65-4572-a552-7a7548fb45b4&name=MM2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Sugar Coated [H.j. Harkins Company, Inc.]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=dd02a11f-6ea6-42e7-b168-bf2b9f4d54ae&name=perphenazine-4.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Cardinal Health]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=abcfeec6-7f3a-4139-a6e6-fa42dafd8264&name=abcfeec6-7f3a-4139-a6e6-fa42dafd8264-02.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Remedyrepack Inc. ]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=0958af4c-87ef-41fd-90a1-ec3e57146945&name=MM2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Remedyrepack Inc. ]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=df20a1fe-bcab-409d-a38e-c211902b440b&name=MM2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Remedyrepack Inc. ]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=20e508cb-20ae-48dc-838a-abe61eb7c0ee&name=MM2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Remedyrepack Inc. ]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=b82a2e03-8eab-4ebb-8988-3d2bf9559c8f&name=MM2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Qualitest Pharmaceuticals]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=5fbfe9da-26e8-4705-98f3-42acd3d7b439&name=perphenazine-2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Remedyrepack Inc. ]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=7cb27d81-ca9d-41e4-b5f1-f944d8af74d0&name=MM2.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [American Health Packaging]](https://www.recallguide.org/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/drug-image-placeholder.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Sandoz Inc]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=6c76e98d-b8c3-441f-bac5-a9de6dc8f14f&name=a6be27a1-466e-4e1c-b7ce-3b3c1c776c06-02.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Clinical Solutions Wholesale]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=20c06f4c-639a-4de3-846f-7754537dc935&name=20c06f4c-639a-4de3-846f-7754537dc935-02.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [State Of Florida Doh Central Pharmacy]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=ea2ba726-0199-42ae-9c60-4b068df35e64&name=b0836c7a-682f-4e63-b7b4-f2a1cbf54d50-01.jpg)
![Perphenazine Tablet, Film Coated [Remedyrepack Inc. ]](http://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/image.cfm?setid=8f4785d6-d267-4037-87e5-31038dcd0c21&name=MM2.jpg)