FDA records indicate that there are no current recalls for this drug.
Are you a medical professional?
Trending Topics
Ultiva Recall
Get an alert when a recall is issued.
Questions & Answers
Side Effects & Adverse Reactions
Itraconazole has been associated with rare cases of serious hepatotoxicity, including liver failure and death. Some of these cases had neither pre-existing liver disease nor a serious underlying medical condition, and some of these cases developed within the first week of treatment. If clinical signs or symptoms develop that are consistent with liver disease, treatment should be discontinued and liver function testing performed. Continued itraconazole use or reinstitution of treatment with itraconazole is strongly discouraged unless there is a serious or life-threatening situation where the expected benefit exceeds the risk. (See PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients and ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
Life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias and/or sudden death have occurred in patients using drugs such as cisapride, pimozide, methadone, or quinidine concomitantly with itraconazole and/or other CYP3A4 inhibitors. Concomitant administration of these drugs with itraconazole is contraindicated. (See BOXED WARNING, CONTRAINDICATIONS, and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.)
Itraconazole Capsules should not be administered for the treatment of onychomycosis in patients with evidence of ventricular dysfunction such as congestive heart failure (CHF) or a history of CHF. Itraconazole Capsules should not be used for other indications in patients with evidence of ventricular dysfunction unless the benefit clearly outweighs the risk.
For patients with risk factors for congestive heart failure, physicians should carefully review the risks and benefits of itraconazole therapy. These risk factors include cardiac disease such as ischemic and valvular disease; significant pulmonary disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; and renal failure and other edematous disorders. Such patients should be informed of the signs and symptoms of CHF, should be treated with caution, and should be monitored for signs and symptoms of CHF during treatment. If signs or symptoms of CHF appear during administration of Itraconazole Capsules, discontinue administration.
Itraconazole has been shown to have a negative inotropic effect. When itraconazole was administered intravenously to anesthetized dogs, a dose-related negative inotropic effect was documented. In a healthy volunteer study of itraconazole intravenous infusion, transient, asymptomatic decreases in left ventricular ejection fraction were observed using gated SPECT imaging; these resolved before the next infusion, 12 hours later.
Itraconazole has been associated with reports of congestive heart failure. In post-marketing experience, heart failure was more frequently reported in patients receiving a total daily dose of 400 mg although there were also cases reported among those receiving lower total daily doses.
Calcium channel blockers can have negative inotropic effects which may be additive to those of itraconazole. In addition, itraconazole can inhibit the metabolism of calcium channel blockers. Therefore, caution should be used when co-administering itraconazole and calcium channel blockers due to an increased risk of CHF. Concomitant administration of itraconazole and felodipine or nisoldipine is contraindicated.
Cases of CHF, peripheral edema, and pulmonary edema have been reported in the post-marketing period among patients being treated for onychomycosis and/or systemic fungal infections. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, CONTRAINDICATIONS, PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions, and ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience for more information.)
Itraconazole has a potential for clinically important drug interactions. Coadministration of specific drugs with itraconazole may result in changes in efficacy of itraconazole and/or the coadministered drug, life-threatening effects and/or sudden death. Drugs that are contraindicated, not recommended or recommended for use with caution in combination with itraconazole are listed in PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.
Itraconazole Capsules and SPORANOX® (itraconazole) Oral Solution should not be used interchangeably. This is because drug exposure is greater with the Oral Solution than with the Capsules when the same dose of drug is given. In addition, the topical effects of mucosal exposure may be different between the two formulations. Only the Oral Solution has been demonstrated effective for oral and/or esophageal candidiasis.
Legal Issues
There is currently no legal information available for this drug.
FDA Safety Alerts
There are currently no FDA safety alerts available for this drug.
Manufacturer Warnings
There is currently no manufacturer warning information available for this drug.
FDA Labeling Changes
There are currently no FDA labeling changes available for this drug.
Uses
Itraconazole Capsules are indicated for the treatment of the following fungal infections in immunocompromised and non-immunocompromised patients:
- Blastomycosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary
- Histoplasmosis, including chronic cavitary pulmonary disease and disseminated, non-meningeal histoplasmosis, and
- Aspergillosis, pulmonary and extrapulmonary, in patients who are intolerant of or who are refractory to amphotericin B therapy.
Specimens for fungal cultures and other relevant laboratory studies (wet mount, histopathology, serology) should be obtained before therapy to isolate and identify causative organisms. Therapy may be instituted before the results of the cultures and other laboratory studies are known; however, once these results become available, antiinfective therapy should be adjusted accordingly.
Itraconazole Capsules are also indicated for the treatment of the following fungal infections in non-immunocompromised patients:
- Onychomycosis of the toenail, with or without fingernail involvement, due to dermatophytes (tinea unguium), and
- Onychomycosis of the fingernail due to dermatophytes (tinea unguium).
Prior to initiating treatment, appropriate nail specimens for laboratory testing (KOH preparation, fungal culture, or nail biopsy) should be obtained to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis.
(See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and ADVERSE REACTIONS: Post-marketing Experience for more information.)
Analyses were conducted on data from two open-label, non-concurrently controlled studies (N=73 combined) in patients with normal or abnormal immune status. The median dose was 200 mg/day. A response for most signs and symptoms was observed within the first 2 weeks, and all signs and symptoms cleared between 3 and 6 months. Results of these two studies demonstrated substantial evidence of the effectiveness of itraconazole for the treatment of blastomycosis compared with the natural history of untreated cases.
Analyses were conducted on data from two open-label, non-concurrently controlled studies (N=34 combined) in patients with normal or abnormal immune status (not including HIV-infected patients). The median dose was 200 mg/day. A response for most signs and symptoms was observed within the first 2 weeks, and all signs and symptoms cleared between 3 and 12 months. Results of these two studies demonstrated substantial evidence of the effectiveness of itraconazole for the treatment of histoplasmosis, compared with the natural history of untreated cases.
Data from a small number of HIV-infected patients suggested that the response rate of histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients is similar to that of non-HIV-infected patients. The clinical course of histoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients is more severe and usually requires maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
Analyses were conducted on data from an open-label, "single-patient-use" protocol designed to make itraconazole available in the U.S. for patients who either failed or were intolerant of amphotericin B therapy (N=190). The findings were corroborated by two smaller open-label studies (N=31 combined) in the same patient population. Most adult patients were treated with a daily dose of 200 to 400 mg, with a median duration of 3 months. Results of these studies demonstrated substantial evidence of effectiveness of itraconazole as a second-line therapy for the treatment of aspergillosis compared with the natural history of the disease in patients who either failed or were intolerant of amphotericin B therapy.
Analyses were conducted on data from three double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (N=214 total; 110 given Itraconazole Capsules) in which patients with onychomycosis of the toenails received 200 mg of Itraconazole Capsules once daily for 12 consecutive weeks. Results of these studies demonstrated mycologic cure, defined as simultaneous occurrence of negative KOH plus negative culture, in 54% of patients. Thirty-five percent (35%) of patients were considered an overall success (mycologic cure plus clear or minimal nail involvement with significantly decreased signs) and 14% of patients demonstrated mycologic cure plus clinical cure (clearance of all signs, with or without residual nail deformity). The mean time to overall success was approximately 10 months. Twenty-one percent (21%) of the overall success group had a relapse (worsening of the global score or conversion of KOH or culture from negative to positive).
Analyses were conducted on data from a double-blind, placebo-controlled study (N=73 total; 37 given Itraconazole Capsules) in which patients with onychomycosis of the fingernails received a 1-week course (pulse) of 200 mg of Itraconazole Capsules b.i.d., followed by a 3-week period without Itraconazole Capsules, which was followed by a second 1-week pulse of 200 mg of Itraconazole Capsules b.i.d. Results demonstrated mycologic cure in 61% of patients. Fifty-six percent (56%) of patients were considered an overall success and 47% of patients demonstrated mycologic cure plus clinical cure. The mean time to overall success was approximately 5 months. None of the patients who achieved overall success relapsed.
History
There is currently no drug history available for this drug.
Other Information
Itraconazole is an azole antifungal agent. Itraconazole is a 1:1:1:1 racemic mixture of four diastereomers (two enantiomeric pairs), each possessing three chiral centers. It may be represented by the following structural formula and nomenclature:
(±)-1-[(R*)-sec-butyl]-4-[p-[4-[p-[[(2R*,4S*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one mixture with (±)-1-[(R*)-sec-butyl]-4-[p-[4-[p-[[(2S*,4R*)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
or
(±)-1-[(RS)-sec-butyl]-4-[p-[4-[p-[[(2R,4S)-2-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-1,3-dioxolan-4-yl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-Δ2-1,2,4-triazolin-5-one
Itraconazole has a molecular formula of C35H38Cl2N8O4 and a molecular weight of 705.64. It is a white to slightly yellowish powder. It is insoluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohols, and freely soluble in dichloromethane. It has a pKa of 3.70 (based on extrapolation of values obtained from methanolic solutions) and a log (n-octanol/water) partition coefficient of 5.66 at pH 8.1.
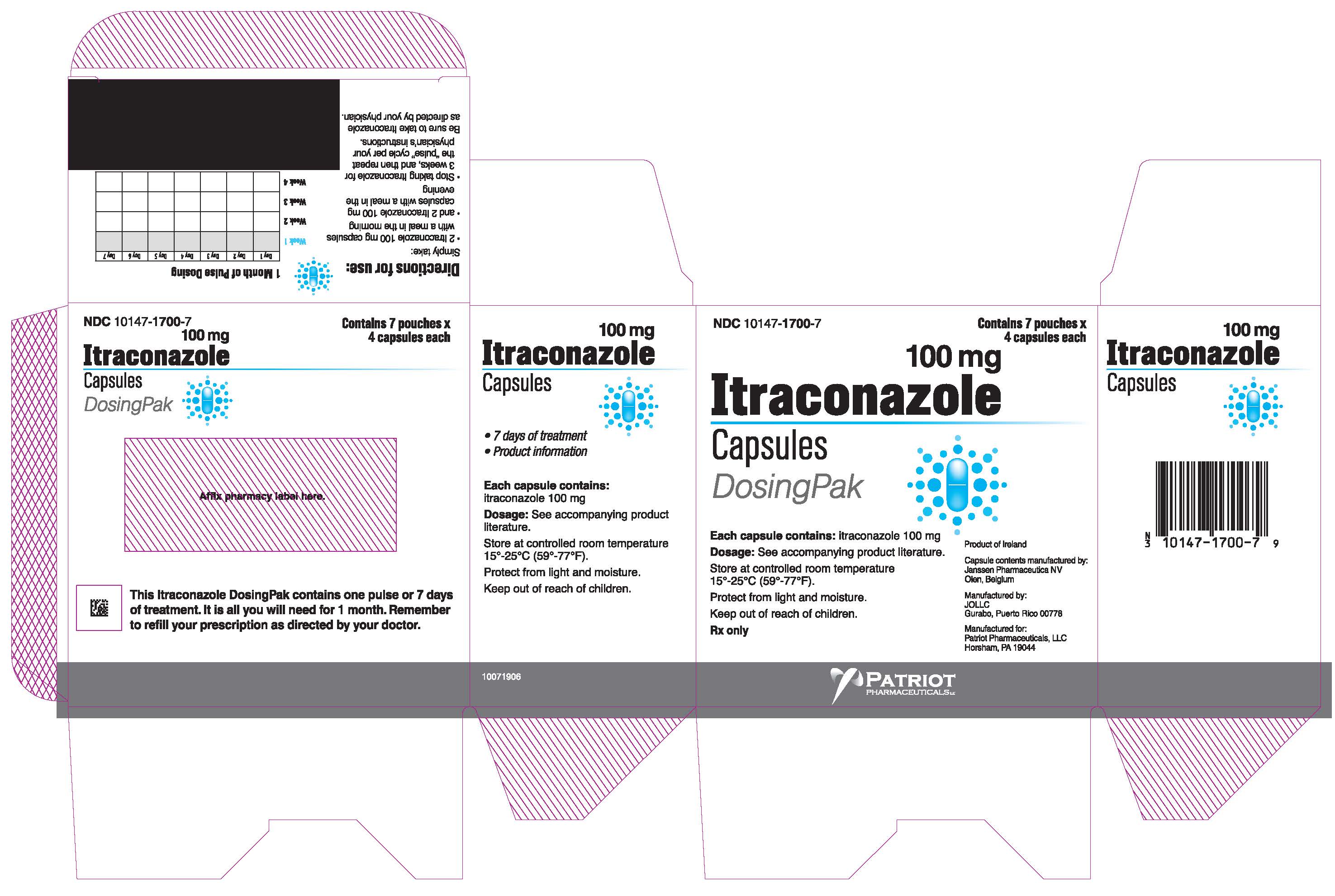
Itraconazole Capsules contain 100 mg of itraconazole coated on sugar spheres (composed of sucrose, maize starch, and purified water). Inactive ingredients are hard gelatin capsule, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol (PEG) 20,000, titanium dioxide, FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Blue No. 2, D&C Red No. 22 and D&C Red No. 28.
Sources
Ultiva Manufacturers
-
Mylan Institutional Llc
![Ultiva (Remifentanil Hydrochloride) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution [Mylan Institutional Llc]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Ultiva | Patriot Pharmaceuticals
![Ultiva (Remifentanil Hydrochloride) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution [Mylan Institutional Llc] Ultiva (Remifentanil Hydrochloride) Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, For Solution [Mylan Institutional Llc]](/wp-content/themes/bootstrap/assets/img/loading2.gif)
Itraconazole Capsules should be taken with a full meal to ensure maximal absorption. Itraconazole Capsules must be swallowed whole.
Itraconazole Capsules are a different preparation than SPORANOX® (itraconazole) Oral Solution and should not be used interchangeably.
Treatment of Blastomycosis and HistoplasmosisThe recommended dose is 200 mg once daily (2 capsules). If there is no obvious improvement, or there is evidence of progressive fungal disease, the dose should be increased in 100-mg increments to a maximum of 400 mg daily. Doses above 200 mg/day should be given in two divided doses.
Treatment of AspergillosisA daily dose of 200 to 400 mg is recommended.
Treatment in Life-Threatening SituationsIn life-threatening situations, a loading dose should be used.
Although clinical studies did not provide for a loading dose, it is recommended, based on pharmacokinetic data, that a loading dose of 200 mg (2 capsules) three times daily (600 mg/day) be given for the first 3 days of treatment.
Treatment should be continued for a minimum of three months and until clinical parameters and laboratory tests indicate that the active fungal infection has subsided. An inadequate period of treatment may lead to recurrence of active infection.
Itraconazole Capsules and SPORANOX® (itraconazole) Oral Solution should not be used interchangeably. Only the oral solution has been demonstrated effective for oral and/or esophageal candidiasis.
Treatment of OnychomycosisToenails with or without fingernail involvement: The recommended dose is 200 mg (2 capsules) once daily for 12 consecutive weeks.
Treatment of OnychomycosisFingernails only: The recommended dosing regimen is 2 treatment pulses, each consisting of 200 mg (2 capsules) b.i.d. (400 mg/day) for 1 week. The pulses are separated by a 3-week period without itraconazole.
Use in Patients with Renal ImpairmentLimited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with renal impairment. Caution should be exercised when this drug is administered in this patient population. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations and PRECAUTIONS.)
Use in Patients with Hepatic ImpairmentLimited data are available on the use of oral itraconazole in patients with hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised when this drug is administered in this patient population. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Special Populations, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS.)
Login To Your Free Account